The goal of the Enterprise Surveys (ES) is to portray the quality of the business environment in the economy by asking a set of questions that capture both the experiences and perceptions of firms. Little is known about what businesses experience in emerging and developing economies and the Enterprise Surveys intend to some extent alleviate this knowledge gap. Below we provide highlights of the recently released data for the Democratic Republic of Congo.
The Democratic Republic of Congo Enterprise Survey covers 529 firms across the West, East, South, and Central regions. Firms interviewed for the ES are formal private firms operating in non-agricultural, non-extractive private sector with 5 employees or more. In addition to the standard Enterprise Survey, data were collected for 412 micro firms (formal firms with 0-4 employees) and 480 informal businesses. In this post we will only focus on a couple of highlights for the standard ES firms. For a more detailed survey highlight please see the following 2-page document.
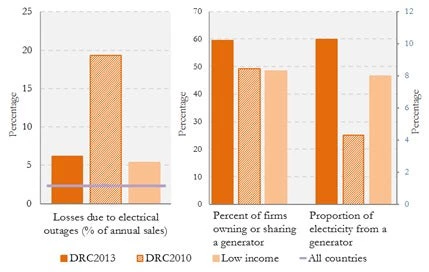
Firms in DRC use generators to compensate for inadequate power provision. Almost 60percent of firms in the Democratic Republic of Congo own or share a generator from which 10 percent of electricity is obtained. Losses experienced by firms due to higher outages are greater than other low income countries, despite declining since 2010. This decline in losses may be due to firms switching to generators (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Firms in DRC use generators to compensate for inadequate provision of electricity
There is also generally a low use of financial services by firms. Only 7 percent of firms use banks to finance investments while 9 percent of firms use banks to finance working capital. These averages are significantly lower than the averages for all countries with ES data. The percent of firms with a checking of savings account is also low (57 percent of firms) and has declined since 2010 when it was at 71 percent. The average for all economies surveyed by enterprise surveys is 88 percent (Figure 2).
Figure 2: Firms in DRC use financial services at a low level, with no improvement since 2010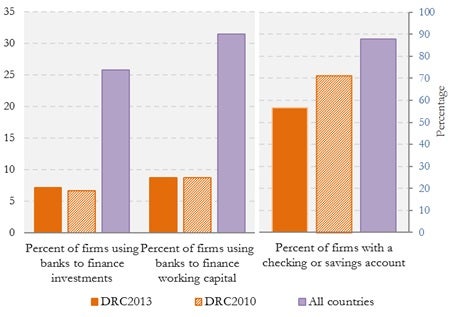
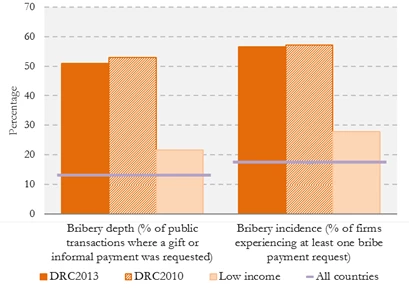
Firms in DRC face a high level of corruption. Bribery incidence -defined as the percentage of firms facing at least one bribe payment request when engaging in six different transactions for public services, permits, or taxes - and bribery depth - the percentage of transactions in which bribes were requested or expected - is significantly higher for firms in the Democratic Republic of Congo than the averages for low income economies or all firms surveyed by Enterprise Surveys. In 2013, 57 percent of firms faced at least one bribe payment request when engaging in six different transactions for public services, permits, or taxes. Furthermore, bribes were requested or expected in one out of two public transactions (Figure 3).
Figure 3: DRC firms face higher levels of corruption than other low income countries
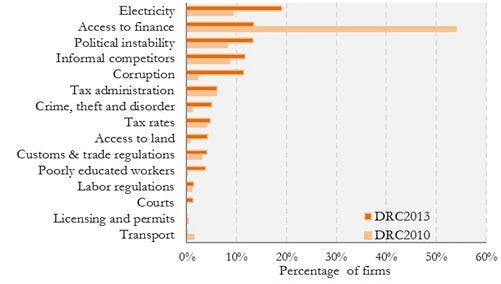
In terms of what firms perceive to be the biggest obstacle out of 15 areas of business environment, firms in DRC tend to rate electricity and access to finance as the top two concerns (Figure 4).
Figure 4: The private sector in DRC considers electricity as the biggest business obstacle
For a full range of indicators please visit the Democratic Republic of Congo survey webpage in the Enterprise Surveys website. The raw survey data can also be obtained here after registration. Please feel free to provide comments, specifically for our survey highlights. Any feedback is much appreciated and may assist us in improving the product.



Join the Conversation