 A woman carrying a child at a community health center in Jakarta, Indonesia.
A woman carrying a child at a community health center in Jakarta, Indonesia.
There is now clear evidence that the devastating economic impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic were distributed unequally among workers in many developed countries. Yet, in the developing world, much less is known about what happened to different types of workers in developing countries. How have they fared during the pandemic?
We recently explored how the crisis has affected different types of workers and find substantial differences. Drawing on phone survey data from about 40 developing countries across five regions, work stoppage rates, for example, ranged between 28% and 37% between April-June 2020 depending on worker type. This complements previous analysis, where we quantified the major adverse effects of the pandemic on the livelihoods of workers across these 40 developing countries, both at its onset and as the crisis evolved.
Looking at groups of workers, phone survey data show that female, young, less educated, and urban workers were most likely to stop work during the early stages of the crisis. Of these, the gender divide was the largest, as women had an 8 percentage point higher chance than men to stop working in the initial phase of the crisis.
Young workers were also harder hit by work stoppage than older adult workers. The difference here is 4 percentage points. Similarly, there is a 4 percentage point gap between low and high educated workers. While the crisis hit urban workers harder than rural workers, in terms of work stoppage rates, the difference was smaller. Here, urban workers were 3 percentage points more likely to stop working than rural workers, indicating that the jobs crisis was not limited to urban areas.
Rate of work stoppage by group
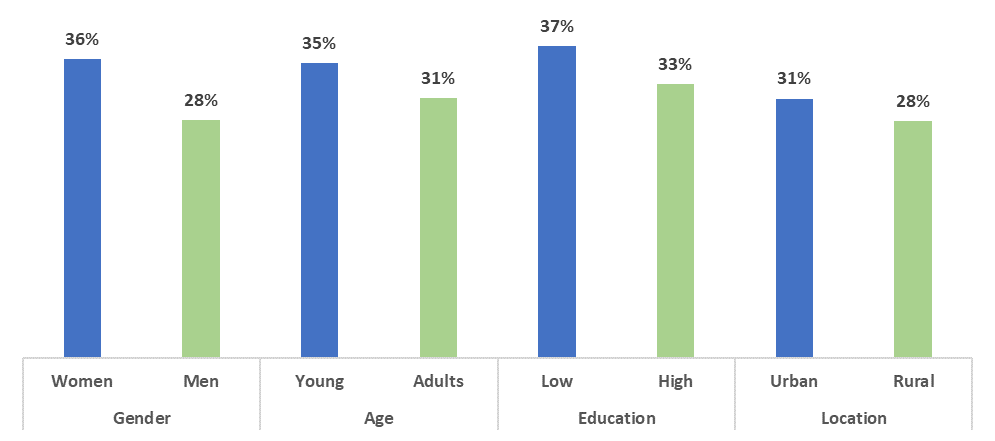
World Bank High-Frequency Phone Surveys 2021.
Dissecting the gender gap
Women were more likely to stop working than men employed in the same economic sectors. Many pundits have noted that women were more likely to be working in industries such as retail, which were heavily impacted by the crisis. While this is true, it explains relatively little of the gender gap in work stoppage.
Similarly, while women also devote more time to child care on average than men, there is little evidence that this was a major factor in leading women to stop work. Rather, the gender gap was primarily caused by female workers being much more likely to stop working than men working in the same sectors. This result seems more consistent with women facing gender discrimination within firms, or working in lower level jobs within firms that were more likely to be cut. Our related working paper sheds more light on that, but further research will be useful to get a better sense of what exactly caused the large gender disparities in work stoppage.
Employment recovery among harder-hit groups
Preliminary results from 17 countries suggest that harder-hit groups may have recovered faster between April and October of 2020. In absolute terms, growth ranged from 13 percentage points for male, urban, and high educated workers, to 16 percentage points for less educated workers. In percent terms, less educated, female, and to a lesser extent, younger workers experienced disproportionately large gains. This indicates that these groups of workers recovered some of the ground lost during the initial phase of the pandemic. Unlike in the US, this recovery was not enough to cause the initial differential impacts to disappear. Furthermore, we do not yet know which types of jobs these initially affected workers obtained, or if their tentative recovery continued into 2021.
Change in employment between April and October, 2020
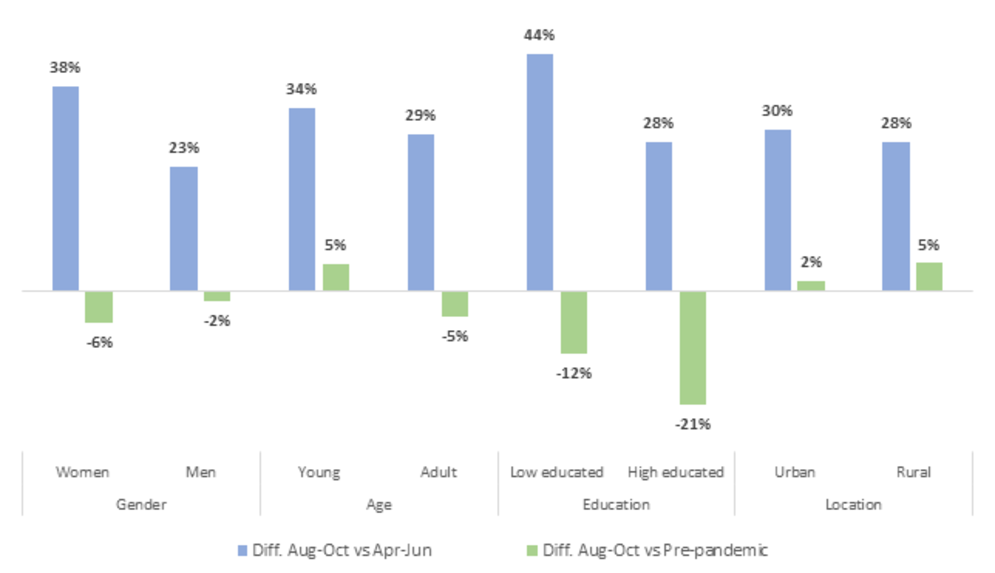
World Bank High-Frequency Phone Surveys 2021.
Part of this tentative recovery may have resulted from the labor market policy response. We have also been collecting information on the social protection and jobs policy responses to the crisis worldwide. From this COVID-19 SPJ policy inventory, we know that developing economies have introduced an unprecedented number of social protection and jobs policies to mitigate the economic impacts of the crisis on workers and their households.
Phone surveys are a good tool
Phone surveys have proven to be surprisingly successful at monitoring group differences in employment loss. Phone surveys have been invaluable to shed light on outcomes during a period when face to face data collection is risky, but they are far from perfect. They tend to overrepresent household heads, which can give a biased picture of employment outcomes.
To get a sense of how much this may be affecting these results on differential impacts, we looked at data for five developing countries that interviewed all respondents in the household and not just heads. In three of these countries, we could make a comparison with phone surveys, while in two others we simulated phone surveys that greatly overrepresented household heads. In almost each case, the phone surveys overestimated employment, but by an equal amount for each group except for age. Therefore, phone surveys, despite their lack of representativeness, are providing a valuable tool for monitoring gender, education, and urban/rural employment disparities.



Join the Conversation