 World Bank / 2022
World Bank / 2022
In 2018, governments around the world spent around $11 trillion—around 12 percent of global GDP— on public procurement. At these substantial volumes, any improvement in public procurement can potentially contribute to savings, integrity, economic growth, inclusiveness, and sustainability. As governments around the world face massive fiscal pressure and rising inflation, they must ensure productive use of public resources—an efficient, transparent, and accountable public procurement is one way of doing so.
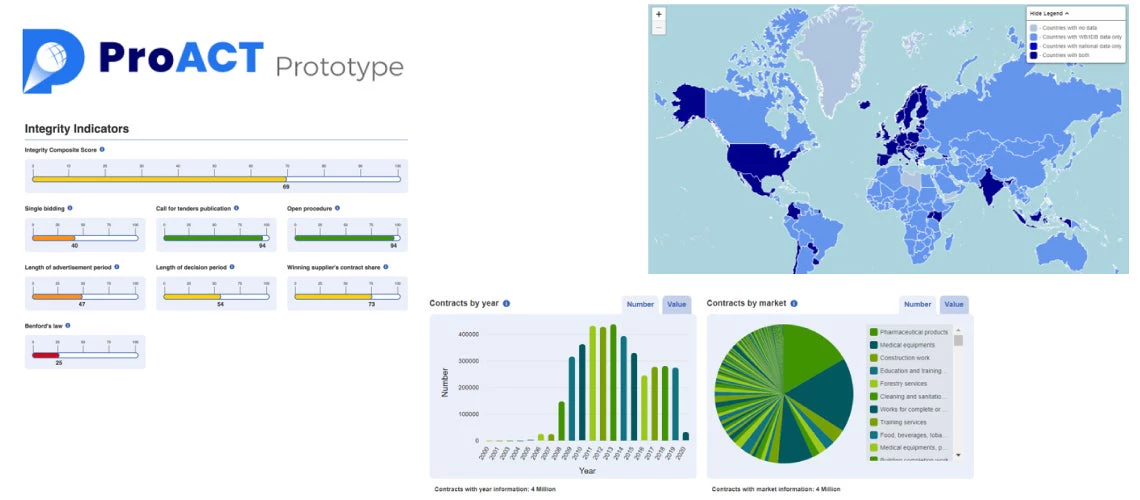
The increasing digitalization of public procurement and openness of government data has created opportunities to build tools to monitor and analyze data globally. Data Analytics tools can support governments in designing effective and efficient procurement policies and strategies. Increasing adoption of e-procurement systems across the world is generating terabytes of digitized data on procurement transactions, while advancements in open government agenda are making this data more accessible to citizens, civil society, and researchers. Building on these global trends, the World Bank in 2021 launched a prototype Procurement AntiCorruption and Transparency platform (ProACT), which has since accumulated over 7,000 unique visitors.
ProACT’s objective is to empower a broad range of users to effectively use public procurement data and generate evidence for strengthening the efficiency, integrity, and probity of public procurement. Currently, ProACT is based on open data from national e-procurement systems from 46 countries and open data on World Bank and Inter-American Development Bank financed contracts for over 100 countries. It allows users to search and analyze specific contracts, tenders, buyers, suppliers and markets. It provides country-level statistics, including competition, transparency and integrity indicators, which can be further disaggregated by sector, procurement method, and contract value range. The platform allows users to download the full datasets underlying ProACT for customized analysis, making it a unique resource for researchers, analysts, and academia. Embracing transparency and replicability, the platform includes a detailed methodology paper and an open ProACT GitHub repository which makes public the code for data construction and analysis.
| |
|
|
|
| Obtain statistics and analysis for contracts, buyers, suppliers, markets and countries |
Download the datasets underlying ProACT for additional analysis
|
Read the methodology paper
|
Replicate and explore the analysis using the code made publicly available on the ProACT GitHub repository |
ProACT is intended for a wide range of users, including procurement officers in national procuring entities; procurement specialists and analysts in MDBs and national Public Procurement Authorities; NGOs that work on procurement, integrity, transparency, and open government; and researchers and academia. For example, ProACT allows procurement officers in national contracting agencies to easily access information from public procurement records outside their own country. This helps them track firms active in public procurement in other countries and analyze international market conditions for specific goods, works and services. ProACT can also provide an initial overview of the public procurement system in a country, and therefore has big potential for applications in core World Bank diagnostics such as Systematic Country Diagnostics, Public Expenditure Reviews, Country Economic Memorandums, and even inform MAPS assessments.
ProACT is part of a broader effort within the World Bank to expand the availability of global indicators on the public sector and therefore sustain evidence-based public sector reforms. The World Bank plays a crucial role in the production and analysis of development data across a variety of ways, such as with the Worldwide Bureaucracy Indicators, the Public Expenditure and Financial Accountability indicators, the MAPS, the GovTech Maturity Index, and the Global Public Procurement Database. As part of this global agenda, ProACT creates, collects, and maintains global public procurement indicators and datasets, and thus strengthens the ability to analyze and support evidence-based procurement reforms. ProACT is also one of the first examples of global indicators sustainably created from administrative data. It can therefore pave the wave for similar endeavors in other sectors aiming to use administrative data to construct global indicators.
ProACT is intended to be a continued effort to generate global data and evidence on public procurement, and it has an exciting future. As more countries adopt e-procurement systems and open up their public procurement data, ProACT will continue to expand its country coverage. ProACT can continue experimenting in bringing together open data related to anticorruption, such as sanctions data and beneficial ownership data that governments are increasingly collecting. Given its reach, and building on synergies from the increasing amount of academic and empirical work on public procurement, ProACT also has the potential to become a collaborative platform between researchers to share data and code.
We invite you to visit and learn about ProACT’s new features. The ProACT team would welcome suggestions on the way forward from readers of this blog and users of the platform and is available to support applications of ProACT. Write us at: proact@worldbank.org.







Join the Conversation