We’re pleased to launch new dashboards in the Health, Nutrition and Population Portal, following the portal’s revamp last year. The renewed HNP portal has two main dashboards covering Population and Health. Both dashboards are designed to be interactive data visualization tools where users can see various population and health indicators. Users can access various charts and maps by selecting specific time, country or region and indicators. We have added new indicators, charts and new health topics such as Universal Health Coverage and Surgery and Anesthesia. Below are some examples of stories gleaned from our dashboards.
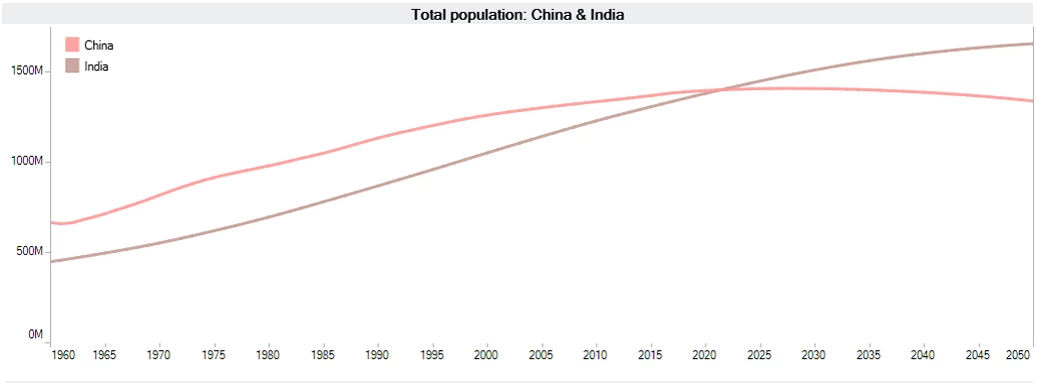
India’s population is projected to surpass that of China around 2022
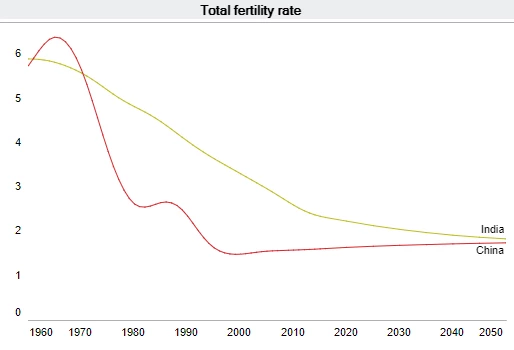
China, with 1.4 billion people, is the most populous country in the world in 2017. However, India, the second most populous country with 1.3 billion people, is projected to surpass China’s population by 2022. China’s total fertility rate (the number of children per woman) has also declined sharply since the 1970s.
http://datatopics.worldbank.org/health/population
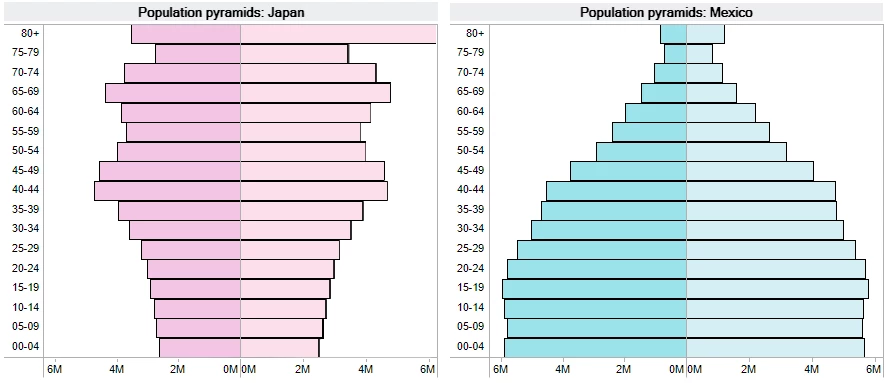
Japan and Mexico are similar in population, but different in age composition
While Mexico and Japan have similar population (129 million and 127 million, respectively) in 2017, the age structures of these countries look very different. The population pyramids of the two countries show that Mexico’s population is much younger than Japan’s. Mexico has more young people and Japan has more old people.
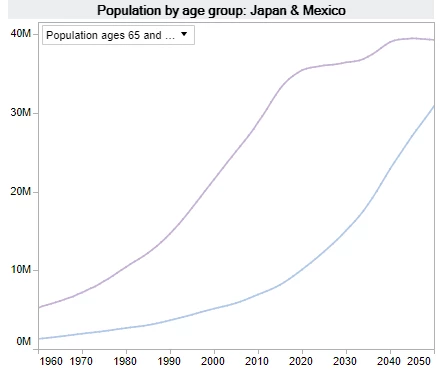
The population ages 65+ has increased rapidly since 1990s in Japan. However, the population ages 65+ in Mexico is projected to exceed 10 million in 2020 and to increase steadily. The differences in the population ages 65 + years between Japan and Mexico is projected to narrow by 2050.
http://datatopics.worldbank.org/health/population
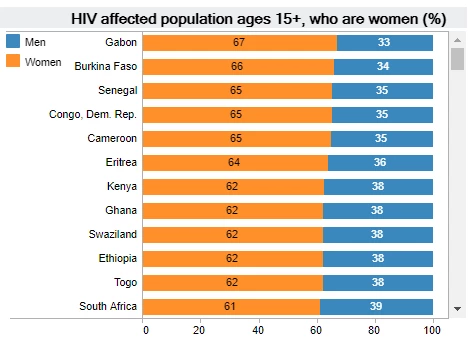
In many Sub-Saharan African countries, women are more affected by HIV/AIDS than men
Women are more vulnerable to HIV than men, especially in Sub-Saharan Africa. In 20 Sub-Saharan African countries, more than 60 percent of the HIV affected population are women. In other regions, less than half of the HIV affected population are women (South Asia: 33%, Latin America and Middle East: 38%). According to the UNAIDS, structural, behavioral and biological factors are compounding the risk of HIV infection among women.
http://datatopics.worldbank.org/health/health
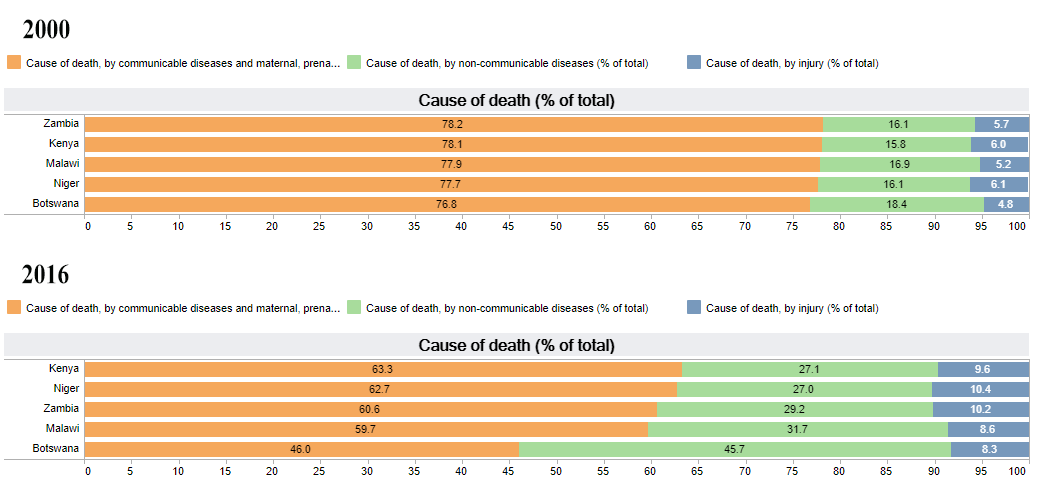
Changes are seen in Cause of Death in low-income countries
Cause of Death is mainly classified into three categories:
- Communicable diseases and maternal, prenatal and nutrition conditions,
- Non-communicable diseases, and
- Injury.
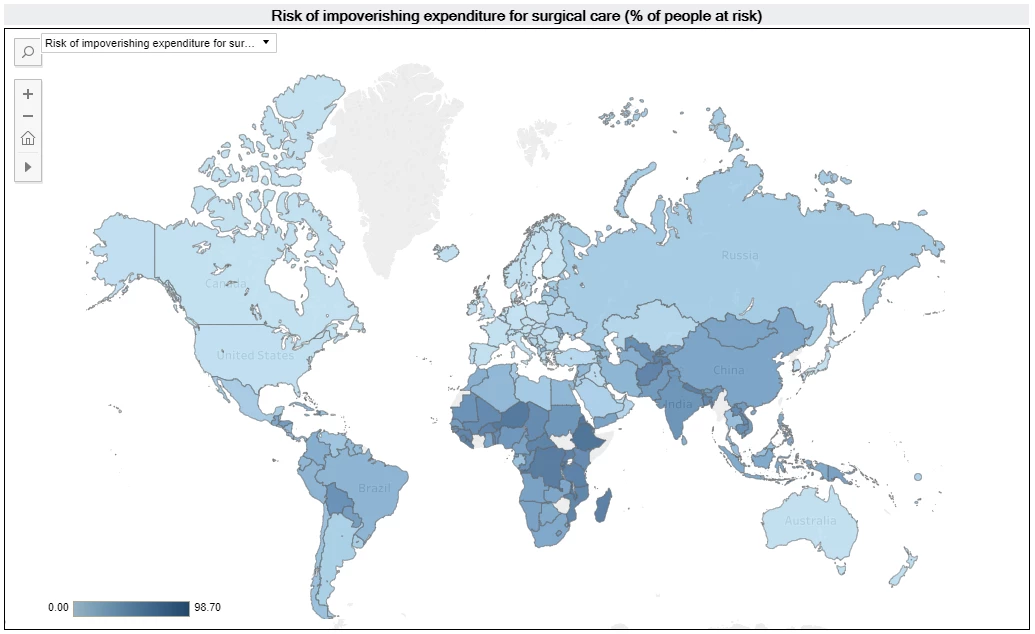
The risk of impoverishing expenditure for surgical care is very low in North America and Europe, but high in Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia
The risk of impoverishing expenditure for surgical care is high in many countries in Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia. The majority of people in these regions cannot afford to pay for surgical care. People in these regions are at risk of being pulled into poverty when they pay for surgical and anesthesia care, due to direct out-of-pocket payments for the care. In North America and Europe the risk is very low because of their risk-sharing system.
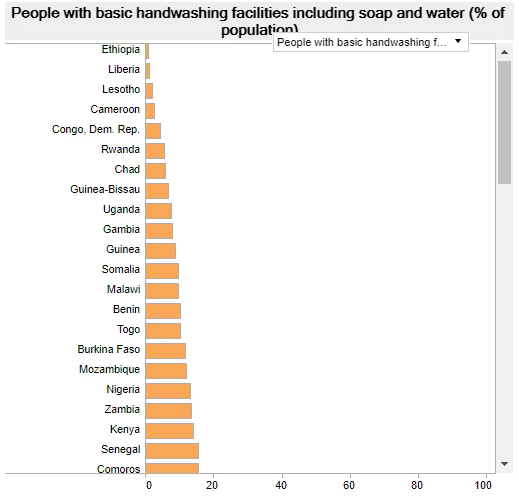
Many people still live in households without basic hand washing facilities
Safe hygiene practices are crucial for human health. Hand washing with soap and water is used to monitor Sustainable Development Goal 6 (Clean water and sanitation), and is considered one of the most cost-effective interventions to prevent diarrhea and respiratory infections, especially among children. In 38 of the 70 countries with data, less than half of the people live in households without basic hand washing facilities in 2015.
http://datatopics.worldbank.org/health/health
These are but a few of the many ways you can use our data and dashboards to tell stories. We encourage you to explore our dashboards, as well as check out the Health, Nutrition and Population Portal.





Join the Conversation