
This blog is part of a series about WITS, the World Integrated Trade Solution, a collaborative trade data platform developed by the World Bank and other institutions. This is the seventh installment of the series—for further reading, here are the first, second, third, fourth, fifth and sixth installments.
Trade policy makers rely on timely, reliable data to make informed decisions and develop effective policies. The World Trade Organization's (WTO) Integrated Data Base (IDB) and Consolidated Tariff Schedules (CTS) offer comprehensive information on tariffs and import data, as reported by governments. Accessible via the WITS interface and WTO data portals, these databases support evidence-based policymaking, market access monitoring, and facilitate negotiations of trade agreements.
The WTO's Integrated Data Base and Consolidated Tariff Schedules
The Integrated Database (IDB), as used and maintained by the WTO, originates from the GATT's (General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade) Tariff Study to aid the Kennedy (1964) and Tokyo Round (1973) negotiations. Officially launched in 1987 for the Uruguay Round, it aimed to store reliable and complete data for tariff negotiations. In 1997, the WTO General Council mandated annual submission of detailed tariff and import statistics, overseen by the WTO Committee on Market Access and improved in 2019 by incorporating technological advancements and enabling automatic data sourcing for quicker updates.
The Consolidated Tariff Schedules (CTS) database contains tariff bindings and specific commitments in agriculture of all WTO Members, consolidating results from past GATT/WTO negotiations and over 700 rectifications and modifications. Tariff bindings are the maximum agreed tariffs that Members can impose on imports from other Members. The CTS database, a working tool with no legal implications, is accessible to WTO Members via the Tariff Analysis Online (TAO) and Goods Schedules e-Library, and to the public at the tariff line level. Each Member's CTS file, in MS-Access and Excel formats, contains its tariff commitments and, if applicable, specific commitments in agriculture. Approved on 27 November 1998 by the Committee on Market Access, the CTS database project aimed to improve recording of Members' concessions on goods through standardized formatting and consolidation.
What does the IDB database contain?
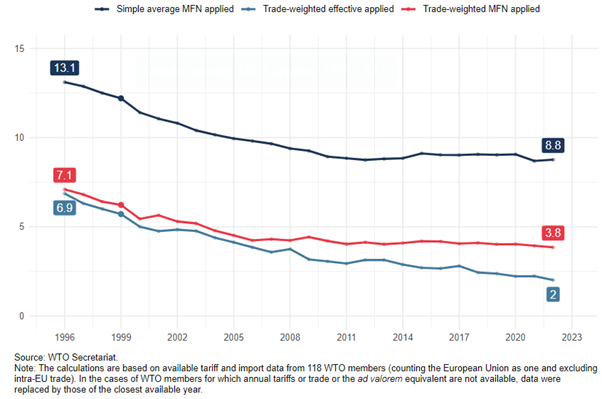
Since its inception, the Integrated Database (IDB) has contained Most Favoured Nation (MFN) applied tariffs as notified by WTO Members and acceding economies. It has expanded to include preferential duties, other charges, and import statistics at the detailed product level. Members are encouraged to notify additional data, such as internal taxes. The database now also records import data by duty schemes, allowing analysis of trade agreements' effectiveness and utilization, following transparency initiatives like the Transparency Mechanism on Preferential Trade Arrangements.
Each WTO Member's dataset includes:
- Annual applied MFN import tariffs (HS codes with 8, 10, or more digits.)
- Import statistics in the same tariff nomenclature, detailing import value (USD) and volume (quantity and unit) by country of origin.
Additional information may include:
- Preferential tariffs under regional trade agreements.
- Non-MFN tariffs (e.g., on imports from non-WTO Members.)
- Ad valorem equivalents (AVEs) of non-ad valorem duties.
- Applied internal taxes and other duties and charges (ODCs.)
- Imports under tariff rate quotas (TRQs) for each relevant tariff line
What does the CTS database contain?
The CTS database compiles WTO Members' concessions on goods from various trade negotiations, including over 700 rectification and modification procedures. These commitments are found in diverse legal instruments, formats and nomenclatures over time, presenting a challenge for standardization. Information sources include pre-Uruguay Round concessions, Uruguay Round concessions, plurilateral agreements, HS transpositions, the "Nairobi package" to eliminate export subsidies, accession packages of new Members, renegotiations through GATT Articles XXIV and XXVIII, and rectifications and modifications of schedules.
The table of tariff commitments for each Member includes:
- Bound MFN tariffs of the latest commitments at the national customs tariff line level (HS-8 digits or more).
- Base MFN tariffs used for tariff reduction commitments not fully implemented.
- Other duties and charges applicable to the tariff line.
- Special safeguards for agricultural products.
- References to the legal instruments where concessions were established.
- Initial negotiating rights (INRs) for present and earlier concessions.
- Implementation period (start year and end year for commitments not fully implemented).
Additional tables provide information on specific commitments in agriculture, including:
- Domestic support commitments (Total AMS) on a per Member basis.
- Export subsidies with bound outlay level and quantity recorded at the tariff line level.
- Tariff quotas, including in-quota bound duty and quota quantity recorded at the tariff line level and linked to out-of-quota bound duty.
What are the standardizations and verifications carried out by the WTO?
The WTO Secretariat undertakes an important task of standardizing the information it receives in a wide range of national formats, which greatly facilitates the aggregation and analysis of data at the global level, and cross-checks the information submitted by Members against other sources. Once verified, it reformats and converts the submitted information to the standardized database formats and coding schemes, including matching the tariffs and imports. The information is then provisional and validated by Member governments to confirm the correctness of the data. Thereafter, most of the information is available to public users.
Keeping the IDB and CTS databases up to date
To maintain their status as the most relevant global data sources of government approved applied and bound tariffs as well as import data, the databases must be continuously updated to incorporate new data and revisions made by WTO Members to their applied tariffs and Schedules of concessions.
Verification, validation, and approval of official data notifications to the IDB is a crucial process to ensure the reliability and credibility of data used for decision-making and trade policy formulation. The verification pipeline confirms accuracy of the data through checks with other sources and consistency over time by established methodologies. Approval signifies endorsement that the data meet specified criteria and can be relied upon for official purposes.
Major updates to the CTS include the Information Technology Agreement (ITA) and the ITA expansion commitments of the participating members and the “Nairobi package” to eliminate agricultural export subsidies. In addition, rectifications and modifications to Schedules of concessions are added to the CTS database whenever they are agreed by Members. Files for newly acceded Members have been created when accessions are concluded.
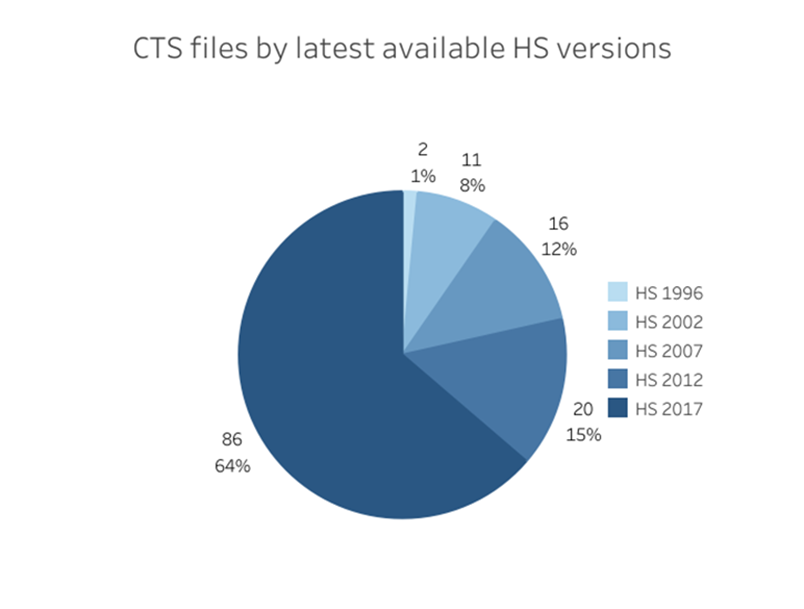
The CTS database is also regularly updated to reflect the agreement by Members to update their Schedules to reflect the most recent HS nomenclatures. The original version of the CTS database was recorded in the HS1996 nomenclature but for most Members their commitments have now been successively transposed into HS2002, HS2007, HS2012 and HS2017 nomenclatures. The next step is to start the transposition exercise to HS2022 nomenclature.
In conclusion, the WTO Integrated Data Base and Consolidated Tariff Schedules play a crucial role in facilitating access to, and analysis of, comprehensive global tariff and import information. By providing standardized and reliable data, it enables governments, policymakers, and analysts to make informed decisions, fostering more effective and strategic trade policies. This contributes significantly to the advancement of global trade and economic cooperation.
Start using the WTO IDB CTS data in https://tao.wto.org/welcome.aspx and or in https://wits.worldbank.org



Join the Conversation