 感受到当前通胀率飙升的不仅有发达经济体,还有绝大部分新兴市场和发展中经济体。
感受到当前通胀率飙升的不仅有发达经济体,还有绝大部分新兴市场和发展中经济体。
*This piece originally appeared in Project Syndicate on February 11, 2022
Today's inflationary surge is being felt not just by the advanced economies but also by the majority of emerging markets and developing economies. And though its causes vary across countries, the task of resolving the problem ultimately will fall to the world's major central banks.
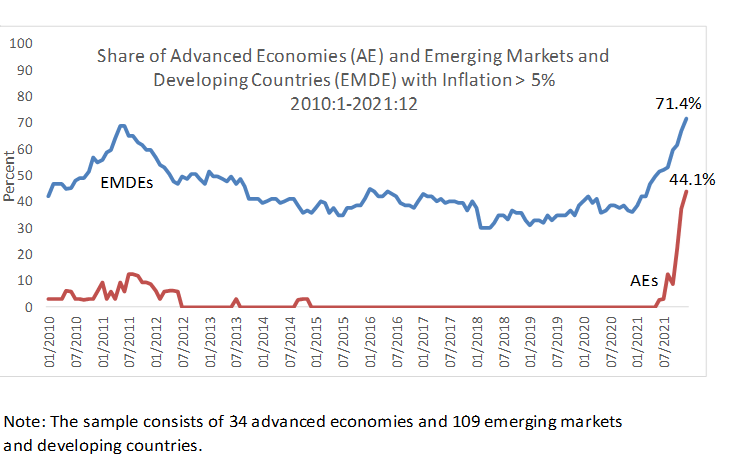
Inflation has come back faster, spiked more markedly, and proved to be more stubborn and persistent than major central banks initially thought possible. After initially dominating headlines in the United States, the problem has become a centerpiece of policy discussions in many other advanced economies. In 15 of the 34 countries classified as AEs by the International Monetary Fund’s World Economic Outlook, 12-month inflation through December 2021 was running above 5%. Such a sudden, shared jump in high inflation (by modern standards) has not been seen in more than 20 years.
Nor is this inflationary surge limited to wealthy countries. Emerging markets and developing economies have been hit by a similar wave, with 78 out of 109 EMDEs also confronting annual inflation rates above 5%. That share of EMDEs (71%) is about twice as large as it was at the end of 2020. Inflation thus has become a global problem – or nearly so, with Asia so far immune.
The primary drivers of the inflation spike are not uniform across countries, particularly when comparing AEs and EMDEs. Diagnoses of “overheating,” prevalent in the US discourse, do not apply to many EMDEs, where fiscal and monetary stimulus in response to COVID-19 was limited, and where economic recovery in 2021 lagged well behind the AE rebound.
In the meantime, the resurgence of inflation will continue to reinforce inequality, both within and across countries.
Moreover, the pandemic-induced bust-and-recovery patterns differ markedly across country income groups, with recovery being defined as an economy’s return to its 2019 level of per capita income. About 41% of high-income AEs met that threshold at the end of 2021, compared to 28% of middle-income EMDEs and just 23% of low-income countries.
But the disparity between advanced and developing economies is even greater than this comparison suggests, because many EMDEs were already experiencing declines in per capita income before the pandemic, whereas AEs were mostly at new highs. While many EMDEs have marked down their estimates of potential output over the past two years, there is little to suggest that their inflationary pressures are driven primarily by overheating in the aftermath of significant policy stimulus.
One development that is common across advanced and developing economies is the increase in commodity prices alongside rising global demand. As of January 2022, oil prices were up 77% from their December 2020 level.
Another major issue affecting advanced and developing economies alike is global supply chains, which continue to be severely affected by the events of the past two years. Transport costs have skyrocketed. And unlike the oil-based supply shock of the 1970s, the COVID-19 supply shocks are more diverse and opaque, and therefore more uncertain, as the World Bank’s most recent Global Economic Prospects stresses.
In EMDEs, currency depreciation (owing to lower inflows of foreign capital and downgrades of sovereign credit ratings) has contributed to inflation among imported goods. And because inflation expectations in EMDEs are less anchored and more attune to currency movements than in AEs, the passthrough from exchange rates to prices tends to be faster and more pronounced.
Another important factor is food price inflation. During 2021, 12-month increases in food prices exceeded 5% in 79% (86 out of 109) of EMDEs. While AEs have not been immune to rising food prices, just 27% of them experienced price hikes exceeding 5%.
Worse, food price inflation also generally hits lower-income countries (and lower-income households everywhere) particularly hard, which makes it tantamount to a regressive tax. Food accounts for a much larger share of the average household consumption basket in EMDEs, which means that inflation in those economies is likely to prove persistent. Today’s higher energy prices will translate directly into higher food prices tomorrow (through higher costs for fertilizer, transport, and so forth).
Although most EMDEs no longer have fixed exchange rates – as they did during the inflation-prone 1970s – the scope for “truly independent” monetary policy in small open economies remains limited, floating exchange rates notwithstanding. The risk of them importing inflation from the global financial centers is not some relic of the past.
Indeed, the most salient feature of today’s inflation is its ubiquity. In the absence of global policy options to resolve supply-chain disruptions, the task of addressing inflation is left to the major central banks. While the US is poised to undergo a modest tightening (by historical standards) in 2022, this is unlikely to be sufficient to rein in price growth. As Kenneth Rogoff and I document in a 2013 paper, much of the inflation persistence of the 1970s stemmed from the US Federal Reserve’s tendency to do too little, too late (until Paul Volcker’s arrival).
To be sure, a more timely and robust policy response from major central banks would not be good news for EMDEs in the short run. Most would experience higher funding costs, and debt crises could become significantly more likely for some. Nonetheless, the longer-term costs of delaying action would be greater. Because the US and other advanced economies failed to tackle inflation quickly during the 1970s, they ultimately needed far more draconian policies, which led to America’s second-deepest post-war recession, along with a developing-country debt crisis.
As the old saying goes, “A stitch in time saves nine.” In the meantime, the resurgence of inflation will continue to reinforce inequality, both within and across countries.



Join the Conversation