
“… If women in rural areas had the same access to land, technology, financial services, education and markets as men, agricultural production could be increased and the number of hungry people reduced by 100-150 million …”
Agriculture Sector: Creating Opportunities for Women
In Afghanistan, agriculture continues to be the backbone of the rural economy – about 70% of the population in rural areas is engaged in on-farm activities. At the same time, large share of the employment generated in non-farm and off-farm sectors, such as manufacturing, are also closely linked to agriculture and food-processing.
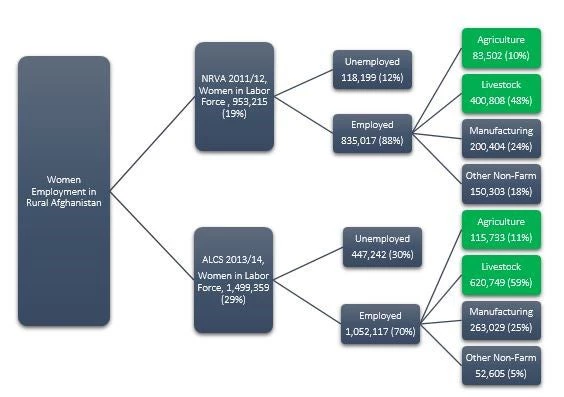
Women’s participation in the labor market has been generally low in rural Afghanistan. For the last decade, the country had one of the world’s lowest rates (19%). In recent years, however, the rural labor market in Afghanistan has experienced an impressive influx of women, increasing the rate to 29%. Yet, a large share of the working-age female in rural Afghanistan (71%) remains out of the labor force. In 2013/14, out of 5.2 million women of age 14 or above, only 1.5 million (29% of total) were in the labor force, about one-third of that 1.5 million workers remained unemployed, and the other two-third were employed – which accounts for only 22% of total rural employment (Figure 1). Of the employed female workers, majority are employed in agriculture (11%) and livestock (59%).
Figure 1: Female Employment and Labor Force Dynamics in Rural Afghanistan (2011-12/2013-14)
Source: Authors’ own calculation using NRVA 2011-12 / ALCS 2013-14
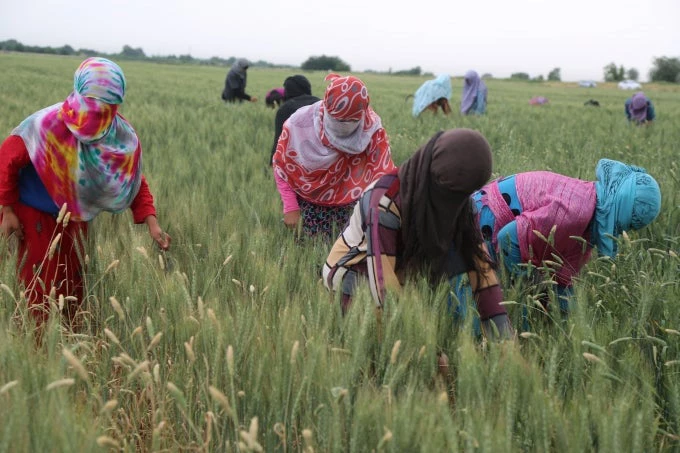
Rural women continue to be the cornerstone of agriculture and food security, and hold the potential to lift their households as well as their communities out of poverty. In the developing world, women comprise over 40 percent of the agricultural workforce (FAO).
Looking Forward: Enabling Women to Increased Access to Agricultural Markets
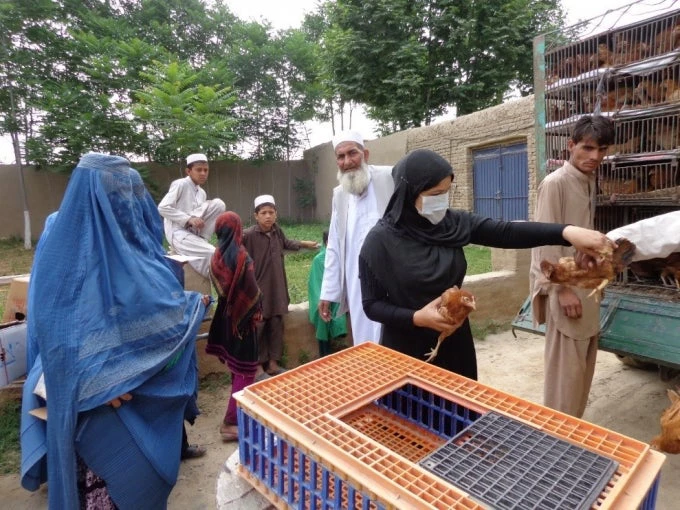
Overall, a dominant share of female workers in agriculture and livestock sectors in Afghanistan is represented as unpaid family workers – those who participate in the economic activities of their households. In 2013/14, about 80% of female employed workers were unpaid family workers. As a result, the average earning of employed female workers has decreased or remained low across rural Afghanistan. The World Bank Group together with the Afghanistan Reconstruction Trust Fund (ARTF) have been supporting the government’s programs to revitalize the agriculture sector to combat poverty and to create more productive and sustainable jobs for rural Afghans.
Most of these programs give special attention to rural women and provide technical and financial support as well as trainings to female workers. The ongoing National Horticulture and Livestock Program and the Afghanistan Rural Enterprise Development Program are two of them. Upcoming programs, such as the Women’s Economic Empowerment – National Priority Program (WEE-NPP), also hold great potential to ensure a more inclusive and dynamic development impact for women in agriculture.





Join the Conversation