 Young workers are using digital platforms to access jobs from all over the globe and embracing online gig work. Copyright: Arne Hoel
Young workers are using digital platforms to access jobs from all over the globe and embracing online gig work. Copyright: Arne Hoel
Can you imagine a job where you can decide where to work, when to work, and which projects to work on? According to our recent data analysis, this is exactly how 243 million youth around the world are challenging the traditional career path, particularly in developing countries where they seek higher pay and jobs that are not easily available close to home.
As explored in the recent World Bank report Working without Borders, many young workers are using digital platforms to access jobs from all over the globe and embracing online gig work rather than pursuing informal, low-quality, local jobs. They are performing task-based jobs facilitated through online gig platforms, continually upgrading their skills, and trying to stay ahead of the competition and evolving technology.
This way of work is rapidly gaining popularity among youth. Online gig work is no longer a fringe activity in the job market, comprising up to 12% of the global labor force. Youth make up over half of this workforce, a percentage that exceeds their relative share of overall workers. By understanding what drives young people to join the online gig economy, policymakers and organizations supporting young people can harness this trend and generate more jobs while empowering youth.
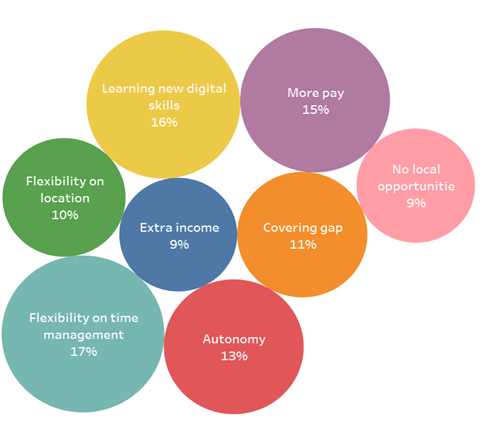
Why are young people breaking with tradition and working online?
According to our report, one of the key reasons young workers are increasingly drawn to online gig work is its inherent flexibility. Online gig work allows students to generate additional income and gain valuable experience in their field while pursuing their studies. Similarly, young professionals at the beginning of their careers can take advantage of the ability to continually upgrade their skills in line with market demands.
In addition to flexibility, online gig work also presents the opportunity to earn higher pay compared to traditional employment. This income potential, coupled with the ability to be one's own boss and access job opportunities in areas where local demand for labor may be low, makes online gig work an attractive proposition for many. It also enables people to cover income gaps and achieve greater financial stability, especially during shock or transition.
Figure 1: Motivations for Youth Participation in Online Gig Work
Where do online gig workers live, and how does internet access affect this trend?
Contrary to a commonly held assumptions, our research revealed that a significant number of online gig workers hail from smaller towns rather than major metropolitan areas. This presents a valuable opportunity for youth living in smaller cities, where there may be few local employment opportunities.
Online gig workers may not need to move to big cities to find work, but they need access to the internet, a reliable connection, and digital devices. In countries with higher internet coverage, the percentage of online gig workers from smaller cities is notably higher, highlighting the importance of expanding internet access to address spatial inequalities in labor markets.
So, is expanding internet access enough? The answer is NO. Our survey found variations across countries with similar levels of internet coverage, suggesting there are barriers to online gig work beyond internet access. For example, in the Middle East and Northern Africa, the share of youth performing online gig work in smaller cities is lower despite higher internet coverage, highlighting untapped potential opportunities.
Figure 2: Internet coverage and the share of young online gig workers in smaller cities

Source: Global Online Gig Workers Survey
What are the benefits of online gigs for different workers?
Online gig work offers better pay and opportunities for young people regardless of their education attainment. For example, in Pakistan's Khyber Pakhtunkhwa region, online gig workers earn more than informal sector workers, even after adjusting for education, age, marital status, and working hours. Our research, however, suggests that in general workers with a college education have a greater chance of accessing higher-paying gigs.
Online gig work also can offer opportunities for young women by providing much-needed flexibility to earn an income while attending to household responsibilities. In many countries, women are better represented in the gig economy than in the offline labor market.
Young gig workers aim to improve their skills, while also earning an income. While technical and digital skills are important, youth also highlight the importance of learning communication and time management skills to be successful as gig workers.
How can we help address potential challenges of online gig work?
While online gig work holds immense potential, most online gig workers – like other informal jobs in developing countries – do not have adequate social protection. While most young gig workers lack access to health insurance or old age benefits, they aspire for more than just traditional social security benefits; they are keen to develop their skills and want financial support for work-related needs such as computers and devices, highlighting the need for targeted social protection programs.
Despite challenges, most young gig workers aspire to grow their careers as online freelancers and want to earn more by freelancing full-time or starting their own agencies. Policymakers and stakeholders can support youth employment and digital skills by providing affordable internet access, digital tools, and training. Policymakers also have an opportunity to partner with online platforms to design innovative programs that expand social protection coverage for informal workers and meet the evolving needs of this dynamic workforce, shaping the future of work.
This blog is part of a Short Notes series that explores findings from the World Bank report “Working Without Borders: The Promise and Peril of Online Gig Work.”
Related blogs
The Promise and Peril of Online Gig Work in Developing Countries
To receive weekly articles, sign-up here




Join the Conversation